Imagine going out for a coffee with a friend. It’s a blistering summer day and you take them to your favorite place with the best iced coffee ever. It’s popular so you have to wait in line. It’s so hot inside that you’re wiping drips of sweat off your forehead. When you get to the front of the line the server apologizes profusely about the broken air conditioning system. The thin coffee shop walls are like a glass house. You order double ice, but it’s too late. You’re sticky with sweat and your favorite experience has been ruined.
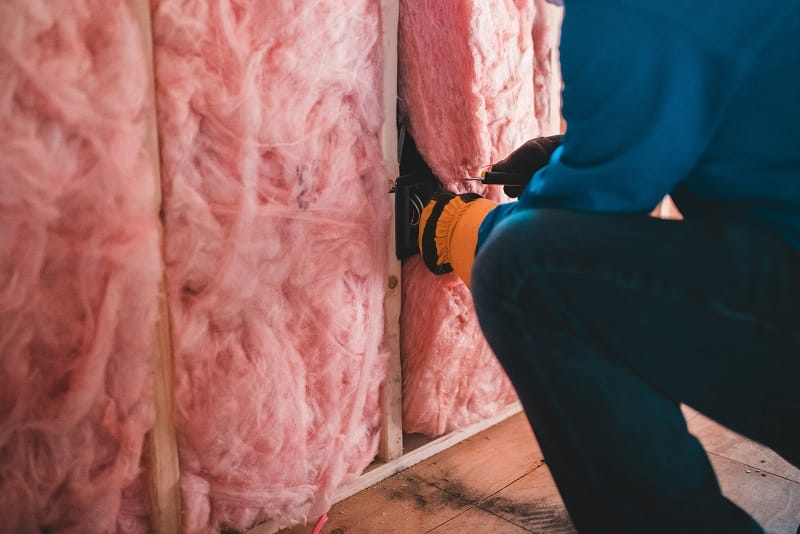
What was this coffee shop missing? Thermal insulation—an often-underestimated hero in the quest for customer comfort and energy efficiency in commercial buildings.
The importance of thermal insulation
When considering energy efficiency for companies, it’s easy to travel down the rabbit hole of more efficient heat pumps and central heating systems. In the summer, thoughts turn to investing in more efficient A/C motors, office fans, or break room fridges. While all of these technologies can affect energy efficiency, without insulation it can be like trying to fill a bucket with holes in it.
The value of insulation is in its versatility as well. You have heaters for cold weather and air conditioning units for hot weather. But rather than relying solely on your army of different temperature regulators, why not increase your insulation? It keeps buildings snug in winter and refreshingly cool in summer. Furthermore, its significance extends beyond comfort—it’s a cornerstone of sustainability and financial prudence.
Consider this fact: heating and cooling account for nearly half of the average household’s energy consumption, according to the U.S. Department of Energy. Yet, with proper insulation, these costs can be slashed by up to 20%, representing a reduction in bills and a tangible contribution to environmental preservation.
Forms of thermal insulation
Thermal insulation takes many forms. Each offers unique advantages suited to different needs and environments.
1. Fiberglass insulation:
Perhaps the most common form, fiberglass insulation comprises fine glass fibers and is renowned for its affordability and effectiveness. It’s ideal for commercial applications, such as insulating attics, walls, and floors, providing excellent thermal resistance.
2. Foam board insulation:
Crafted from polystyrene or polyurethane, foam board insulation offers superior thermal and moisture resistance. Its rigid panels make it suitable for insulating walls, roofs, and foundations, providing seamless coverage and enhanced energy efficiency.
3. Cellulose insulation:
Cellulose is made from recycled paper and plant fibers. This insulation is an eco-friendly option that offers excellent thermal performance. It can be blown into walls, attics, and floor cavities, conforming to irregular shapes and providing efficient insulation.
4. Spray foam insulation:
Known for its expansive nature, spray foam insulation forms an airtight seal upon application, preventing air infiltration and heat loss. It’s perfect for sealing gaps, cracks, and hard-to-reach areas, offering unparalleled efficiency in both residential and commercial settings.
Which to use?
Each type of insulation has its strengths and is better suited for particular situations. Fiberglass insulation, for example, is cost-effective and easy to install, making it a popular choice for offices and receptions.
Foam board insulation, with its superior thermal resistance, is ideal for areas with limited space, such as closets or storage rooms.
Cellulose insulation, known for its eco-friendliness, is preferred by environmentally-conscious homeowners seeking sustainable solutions.
Meanwhile, spray foam insulation excels in sealing air leaks and providing maximum energy savings, making it a favorite for energy-conscious consumers.
Industrial insulation
Beyond commercial applications, thermal insulation is crucial in industrial settings, particularly in machinery insulation. Industrial equipment, such as boilers, furnaces, and piping systems, can get really hot, which, if not properly insulated, can lead to energy loss and operational inefficiencies. On the flipside, ice rinks, food production, and transport, and some chemical reactions require super cold environments. Without proper insulation, these can be expensive to maintain.
Hot stuff
Industrial machinery insulation uses specialized materials to withstand high temperatures and harsh operating conditions. Insulating materials such as ceramic fibers, mineral wool, and high-temperature coatings are employed to minimize heat transfer and enhance equipment performance.
Keep your cool
Since heat can’t travel through the air very easily, one of the best ways to keep things cool is to create a layer of air between the cold and the hot. Similarly, door designs, like having two automatic sliding doors, can limit airflow into a store, insulating the interior.
By insulating industrial spaces and machinery, companies can improve energy efficiency, reduce operating costs, and prolong equipment lifespan. Moreover, effective insulation contributes to a safer work environment by reducing the risk of heat-related accidents and minimizing thermal exposure to workers.
Maximizing insulating benefits
As we navigate the challenges of climate change and escalating energy costs, thermal insulation emerges as a sign that we can maintain comfort without losses to the environment or the bank account. It’s not just about staying warm in winter or cool in summer—it’s about getting the most benefit out of the energy for which we are paying. By embracing thermal insulation in commercial and industrial settings, we create a world where the effect of our energy usage has less adverse effects on the environment.
Others articles you might like
Six factors that affect energy prices
Every business leader knows how important it is to understand and predict operating costs. Your projected budget shows what your future fina...
25 January 2024Six advantages of green energy and microgeneration for companies
Most companies rely partly or entirely on non-renewable fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, to heat and cool their facilities and to ...
9 January 2024Six ways to retrofit your business for energy efficiency
With energy bills getting harder to manage and budget for, more business leaders think about ways to use less energy. Prioritizing your comp...
5 December 2023